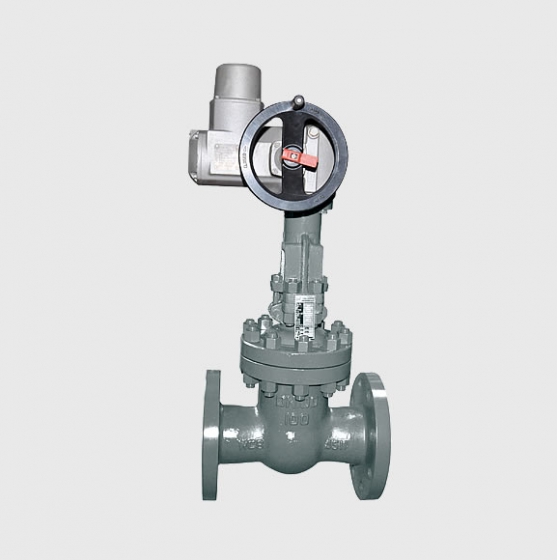
| model | G101/G102/G103/G104/G105/G106 |
| Nominal diameter | 1/2″~8″ (15A~200A) |
| Nominal pressure | ANSI Class 150~600#; PN1.0MPa~PN10.0MPa |
| Medium temperature | -196℃~538℃ |
| Flange distance | Refer to the selection sample |
| Connection | • Flange type (RF, FM, RTJ) • Welding type (SW below 50A, BW above 80A) |
| Valve core shape | •P hole single seat •Q hole single seat |
| Flow characteristics | •Equal percentage •Linear •Switch |
| Valve body material | WCB, LCB, WC6, WC9, CF8, CF8M, CF3M and other alloy steels |
| Leakage | •Hard seal: ANSI Class Ⅳ, Ⅴ •Soft seal: ANSI Class Ⅵ |
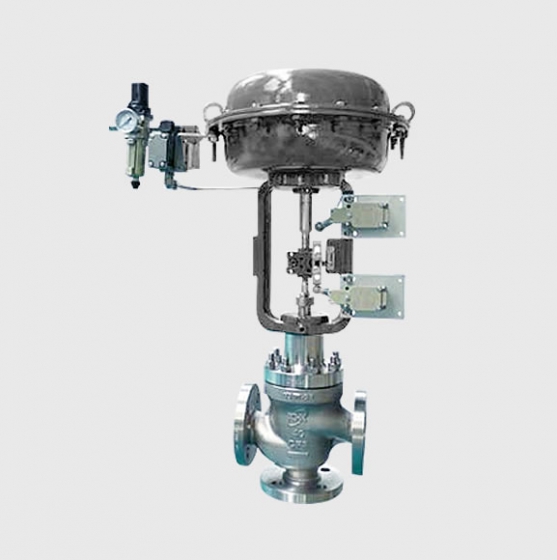
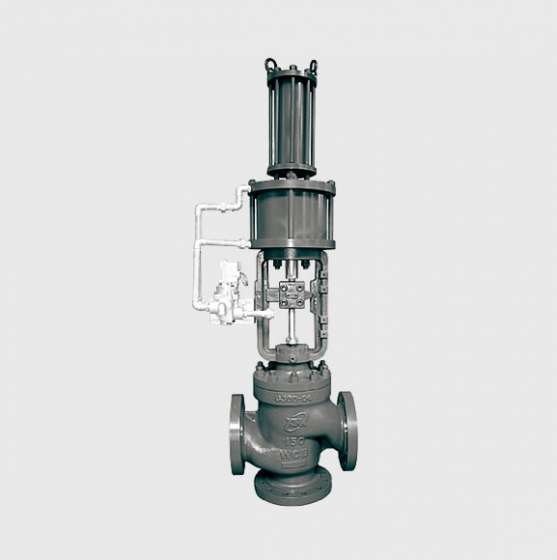
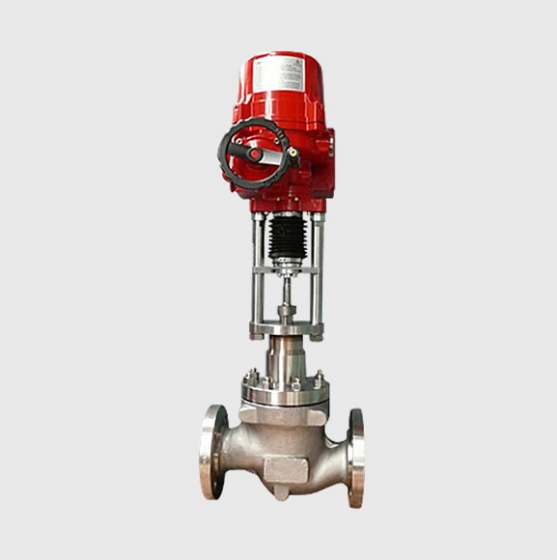
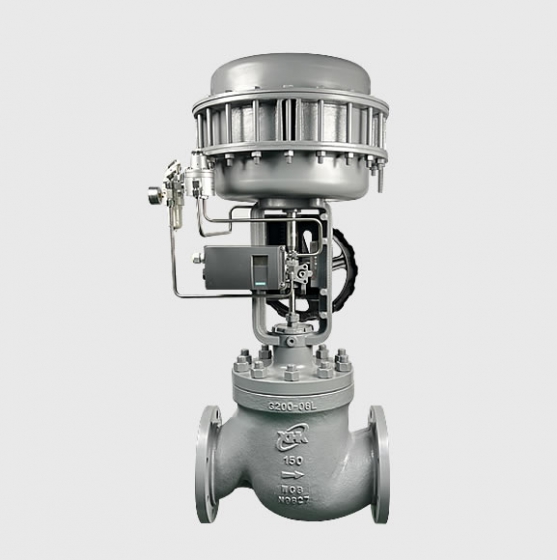
| Actuator | • Pneumatic diaphragm actuator • Pneumatic piston actuator • Fully electronic actuator |
| Surface coating | Dark green epoxy resin When the valve body is made of stainless steel, the body is not coated |
Regulating valves with actuator mechanisms are core equipment in industrial automation control systems. They mainly consist of valve bodies, valve cores, actuators, and controllers. By driving the valve core through the actuator, precise regulation of fluid flow, pressure, temperature, and other parameters is achieved. The following explanation will be carried out from three aspects: technical principles, application industries and cases, and image resources.
I. Technical Analysis of Control Valves with Actuators
1. Types and Characteristics of Actuators
– **Pneumatic Actuators**: Powered by compressed air, they have a fast response time (about 0.1-0.5 seconds), excellent explosion-proof performance, and are suitable for hazardous environments such as petrochemicals. Typical products include pneumatic diaphragm control valves, which feature a multi-spring design, reducing weight by 30% compared to traditional models and increasing flow capacity by 30%.
– **Electric Actuators**: Driven by motors, they offer high control accuracy (regulation error ≤ ±1%), support remote communication (such as HART, Profibus), and have low maintenance costs. For instance, Siemens’ intelligent electric control valves integrate PID control modules, enabling adaptive regulation.
– **Hydraulic Actuators**: They provide large output torque (up to tens of thousands of Newton-meters), making them suitable for high-pressure, large-diameter valves (such as DN1000 and above), commonly used in metallurgy, water conservancy, and other fields.
2. Valve Body Structure and Function
– **Straight-through single-seat valve**: It has excellent sealing performance (leakage rate ≤ 0.01%Kv), but the unbalanced force is relatively large. It is suitable for small diameter and low differential pressure applications.
– **Tubular valve**: It has strong anti-cavitation performance and a large flow capacity. It is widely used in steam regulation for power station boilers.
– **Eccentric rotary valve**: The valve core spherical surface and the valve shaft have an eccentric distance, resulting in a small opening and closing torque. It can regulate high-viscosity or particle-containing media, such as the T8210 model acid and alkali resistant control valve from Japan’s TOKO.
– **Sanitary control valve**: Made of 316L stainless steel, with a surface roughness of Ra ≤ 0.8μm, it complies with EHEDG and 3A standards and is used for aseptic control in the food and beverage and pharmaceutical industries.
3. Key Technology Development
– **Intelligentization**: Integrated sensors and diagnostic systems can monitor the valve status in real time (such as leakage and wear) and predict faults through AI algorithms. For instance, the large flow balanced three-way regulating valve of Shandong Feite improves the regulating stability through patented structural design.
– **Energy conservation**: The low-S energy-saving regulating valve optimizes the flow channel design to maintain high efficiency under low pressure difference, reducing energy consumption by 20% to 30%.
– **Safety**: Safety Instrumented System (SIS) requires valves to have high reliability. For example, the large pressure difference molten salt regulating valve of Yahe Valve Industry solves the vibration problem in solar thermal power plants through material hardening treatment, extending the operating life to more than five years.
II. Industry Applications and Typical Cases of Self-Regulating Valves
1. Petrochemical Industry
– **Application Scenarios**: Temperature control of reaction vessels, pressure regulation of distillation columns, and optimization of crude oil distillation flow.
– **Case**: A certain chemical plant adopted intelligent pneumatic control valves. By real-time monitoring of the pressure and temperature of the reaction vessel and automatically adjusting the feed rate, the product qualification rate was increased from 85% to 98%, and energy consumption was reduced by 15%.
2. Power Industry
– **Application Scenarios**: Boiler water level control, steam turbine bypass system, molten salt flow regulation in solar thermal power plants.
– **Case**: The 100MW solar thermal power plant in Dunhuang, operated by Shouhang, adopted 24″ high differential pressure control valves from Yahu Valve Industry. This solved the long-standing vibration problem. The valves have been in operation for six months without leakage, and efficiency has increased by 12%.
3. Pharmaceutical and Food & Beverage Industries
– **Application Scenarios**: Aseptic filling flow control, high-temperature sterilization steam regulation, nitrogen seal pressure maintenance for storage tanks.
– **Case Study**: A biopharmaceutical company utilized electric diaphragm control valves with PTFE linings to precisely control the flow of culture media (with an error of ≤±0.5%), while meeting GMP hygiene requirements.
4. Water Treatment Industry
– **Application Scenarios**: Flow regulation in aeration tanks of sewage treatment plants, pressure control in seawater desalination systems.
– **Case Study**: In a project at a chemical plant in Dongying, Shandong, the control valve optimized the dosing flow through an adaptive algorithm, increasing the COD removal rate of wastewater from 70% to 85% and reducing chemical consumption by 25%.
5. Metallurgical Industry
– **Application Scenarios**: Pressure regulation of blast furnace gas, control of cooling water for continuous casting molds.
– **Case**: A certain steel plant adopted electro-hydraulic linkage control valves, achieving rapid response (response time ≤ 0.3 seconds) in the hydraulic system of the steel rolling workshop, and improving the rolling accuracy to ±0.01mm.
 Baisteels
Baisteels